Deep sea sharks are captivating creatures that inhabit the darkish depths of our oceans. Known for their particular versions and numerous species, those sharks play a crucial function in maintaining the steadiness of marine ecosystems.
This article will delve into the region of deep sea sharks, highlighting their characteristics, behaviors, and the threats they face. We’ll additionally discover the significance in their conservation.
Key Takeaways
- Deep sea sharks are vital to marine ecosystems.
- They possess precise permutations for survival in excessive environments.
- Many species of deep sea sharks are threatened with the beneficial useful resource of human sports activities activities.
- Conservation efforts are vital to guard those enigmatic creatures.
What Are Deep Sea Sharks?
Deep sea sharks are species that stay at depths extra than 200 meters (656 feet). These sharks have tailor-made to existence in an surroundings with excessive strain,
low light, and cold temperatures. Some famous deep sea shark species embody the Goblin Shark, Frilled Shark, and Basking Shark.

Characteristics of Deep Sea Sharks
Deep sea sharks show off numerous specific characteristics:
- Bioluminescence: Some species can produce slight to attract prey or speak.
- Large Eyes: Adapted to low-mild conditions, deep sea sharks often have huge eyes.
- Slow Growth Rates: Many deep sea sharks develop slowly, making their populations vulnerable to overfishing.
The Importance of Deep Sea Sharks in Ecosystems
Deep sea sharks are apex predators, which means that that they will be on the pinnacle of the meals chain.
They help manage the populace of different marine species, ensuring a balanced surroundings. This is important for the fitness of the oceans.
The Diversity of Deep Sea Sharks
Common Species of Deep Sea Sharks
- Goblin Shark: Known for its first-rate protruding jaw and flat snout, the Goblin Shark is regularly known as a “dwelling fossil.”
- Frilled Shark: With an prolonged, eel-like frame and frilled gills, this shark is frequently referred to as a “dwelling fossil” as properly.
- Basking Shark: The 2nd-largest shark species, it’s miles a easy out feeder, typically consuming plankton.
| Species | Habitat Depth | Diet | Notable Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goblin Shark | 100m to 1,200m | Fish and cephalopods | Protruding jaw |
| Frilled Shark | 200m to 1,200m | Fish and squid | Frilled gills |
| Basking Shark | 200m to 1,200m | Plankton | Largest filter feeder |
Adaptations for Survival
Deep sea sharks have evolved several variations to thrive of their environment:
1. Sensory Adaptations
Deep sea sharks have heightened senses. Their huge eyes help them see in the darkish, and they’re capable of find out electric fields via specialised organs called ampullae of Lorenzini.
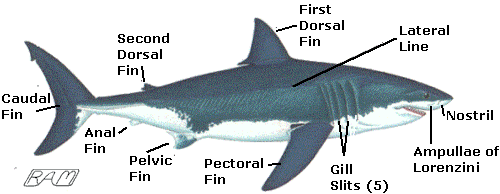
2. Physical Adaptations
Their our bodies are streamlined, deliberating efficient swimming in bloodless, dense water. Many deep sea sharks have additionally advanced specific body shapes and colorations for camouflage and searching.
3. Feeding Strategies
Deep sea sharks appoint numerous feeding strategies. Some are ambush predators, while others are filter feeders much like the Basking Shark, which swims with its mouth open to seize plankton.
Threats to Deep Sea Sharks
Despite their adaptations, deep sea sharks face severa threats:
Overfishing
Many deep sea sharks are targeted for their fins, meat, and liver oil. Overfishing has led to drastic populace declines in numerous species.
Habitat Destruction
Deep sea mining and pollution have damaging consequences on shark habitats. The destruction of ocean floor ecosystems affects the entire meals chain.
Climate Change
Rising ocean temperatures and acidification threaten the survival of deep sea sharks through converting their habitats and meals sources.

Conservation Efforts
Importance of Conservation
Conserving deep sea sharks is critical for the fitness of marine ecosystems. Protecting their populations allows hold the stability of ocean lifestyles.
Organizations and Initiatives
Various businesses are running in the direction of the conservation of deep sea sharks. Initiatives encompass:
- Marine Protected Areas: Establishing zones wherein fishing and distinct human sports are constrained.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing studies to understand shark populations and behaviors is vital for powerful conservation.
The Role of Deep Sea Sharks in Human Culture
Deep sea sharks have intrigued people for hundreds of years. They function in folklore, literature, and famous media, regularly depicted as fearsome creatures.
However, information their authentic nature is crucial for fostering respect and promoting conservation.
Future of Deep Sea Sharks
The destiny of deep sea sharks relies upon on our moves these days. Increased attention and conservation efforts can assist shield those exquisite creatures.
Sustainable fishing practices and stricter regulations are important to make certain their survival.

1. Goblin Shark
Overview
The Goblin Shark is often known as a “residing fossil.” Its one of a kind flat snout and sticking out jaw make it look like some thing out of a nightmare.
Distinctive Features
- Protruding Jaw: This shark can make bigger its jaw forward to seize prey speedy.
- Color: Its pale crimson skin gives it an otherworldly appearance.
Habitat
Typically located at depths of one hundred to 1,two hundred meters, the Goblin Shark dwells in deep waters, making it not often seen by human beings.
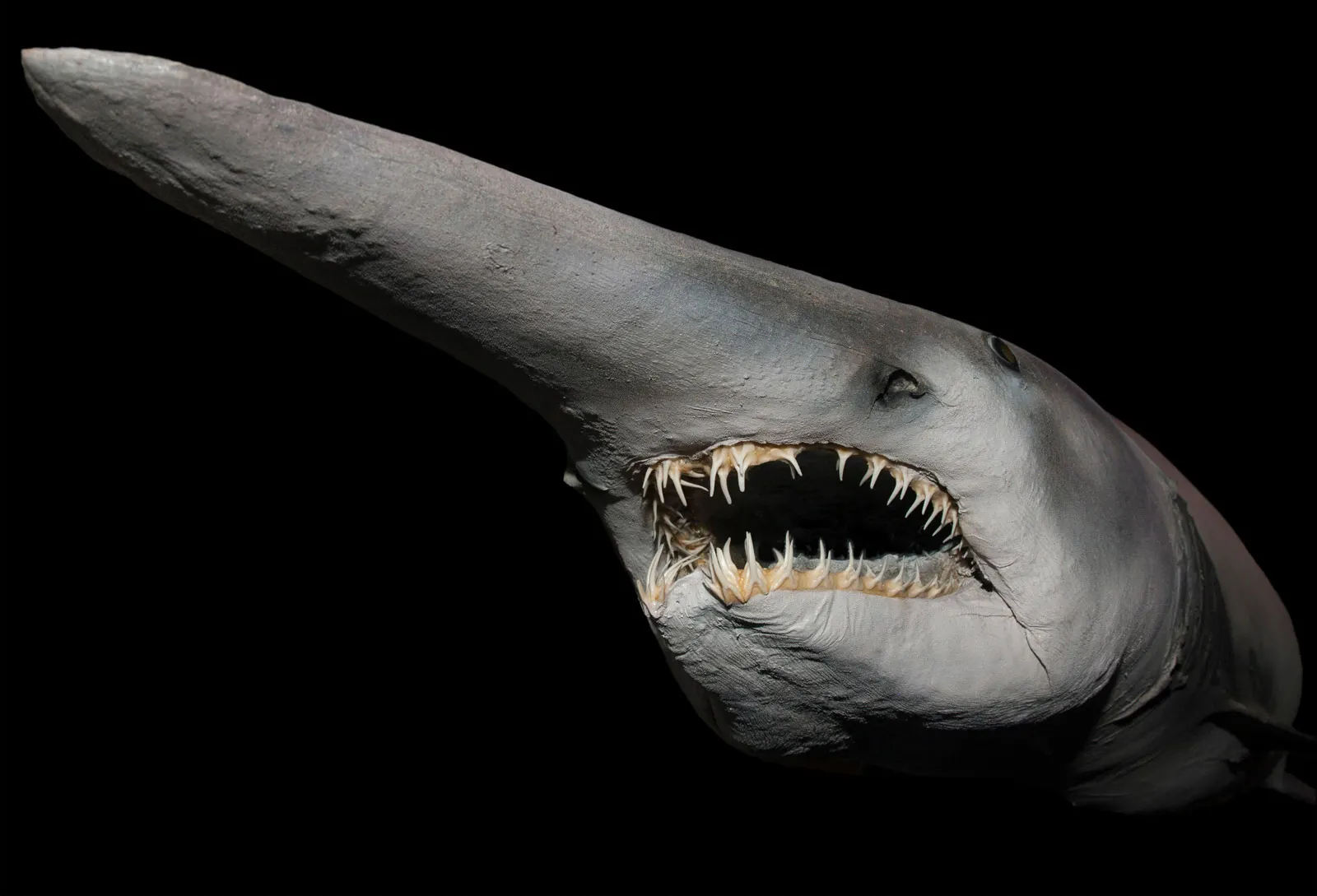

2. Frilled Shark
Overview
Known for its elongated frame and frilled gills, the Frilled Shark looks more like a legendary sea serpent than a traditional shark.
Distinctive Features
- Frilled Gills: Its gills are included in frilled tissue, comparable to a mane.
- Eel-like Body: This shark has a long, narrow frame which can develop up to two meters.
Habitat
Frilled Sharks pick deep waters, frequently observed at depths of 2 hundred to 1,two hundred meters.
3. Sleeper Shark
Overview
The Sleeper Shark won’t be as visually hanging as others, however its sluggish way of life and deep-sea habitat give it an eerie reputation.
Distinctive Features
- Blunt Head: The Sleeper Shark has a large, flattened head that adds to its unsettling look.
- Size: They can reach lengths of up to 4 meters.
Habitat
These sharks are normally located in deep, cold waters, frequently at depths of 200 to two,000 meters.

4. Lantern Shark
Overview
Named for its capability to produce light, the Lantern Shark is one of the smallest deep-sea sharks, however its sparkling functions may be pretty unsettling.
Distinctive Features
- Bioluminescence: This shark emits light from its frame, which it uses to draw prey and communicate.
- Size: Most species are about 1 meter lengthy, making them especially small.
Habitat
Lantern Sharks inhabit deep waters around the sector, generally discovered at depths of 200 to one,two hundred meters.
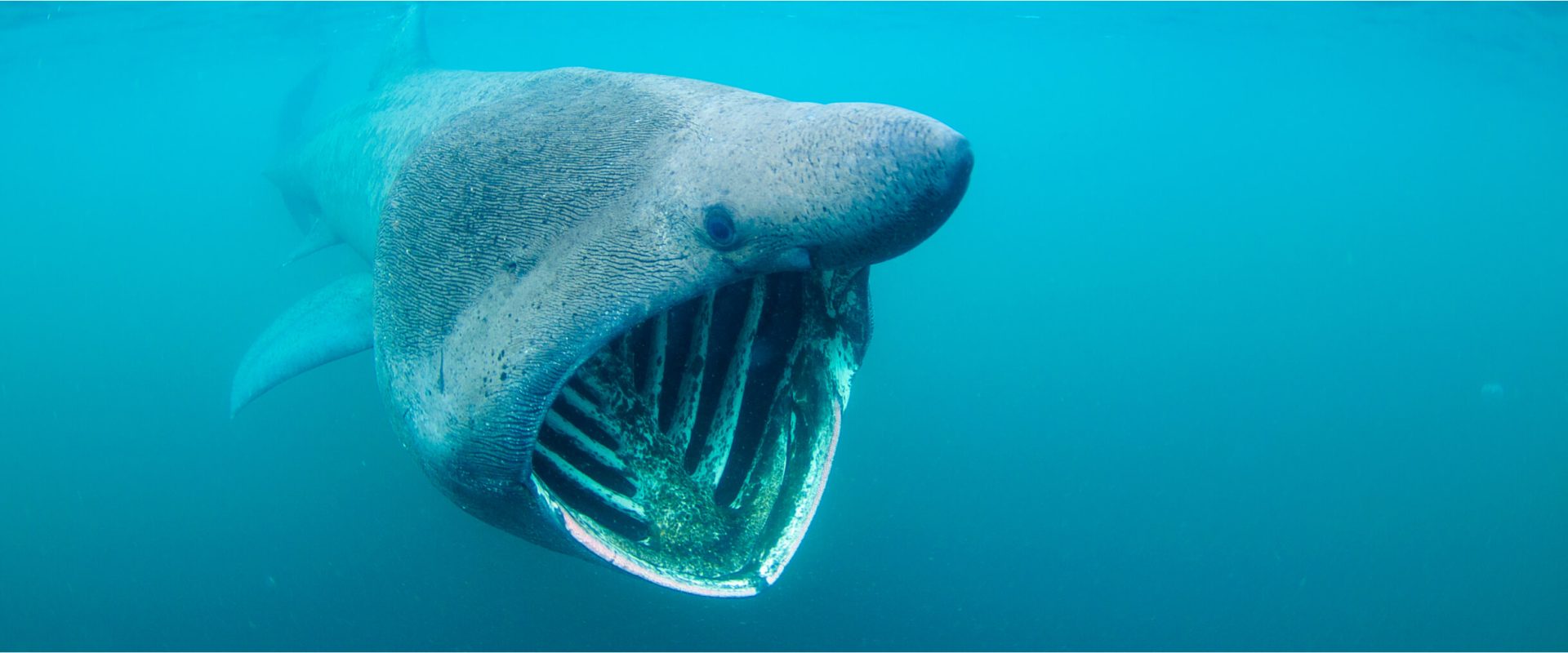
5. Basking Shark
Overview
While the Basking Shark is a clear out feeder and poses no threat to people, its massive size and unique look may be quite intimidating.
Distinctive Features
- Size: The Basking Shark can grow as much as 12 meters lengthy, making it the second one-biggest shark species.
- Large Mouth: Its wide mouth is used to filter out plankton, giving it a ghostly visage whilst open.
Habitat
These sharks inhabit temperate seas and can be determined in depths ranging from floor waters to at least one,200 meters.

6. Dogfish Shark
Overview
The Dogfish Shark won’t appearance especially frightening in the beginning glance, but its sharp enamel and predatory nature make it an impressive hunter.
Distinctive Features
- Spines: Many species have spines on their dorsal fins that can be quite painful.
- Sharp Teeth: Their tooth are designed for grasping slippery prey.
Habitat
Dogfish Sharks are found in various depths, normally from shallow waters to about 1,500 meters deep.
7. Hammerhead Shark
Overview
The Hammerhead Shark, specially the Great Hammerhead, is thought for its unusual head shape, which may be pretty intimidating.
Distinctive Features
- Hammer-fashioned Head: This precise feature offers better sensory belief and allows in hunting.
- Size: Great Hammerheads can reach lengths of up to 6 meters.
Habitat
While they can be found in shallower waters, some species venture into deeper parts of the ocean, usually round 2 hundred meters.
FAQs About Deep Sea Shark
What is the inner most shark?
The Goblin Shark is regularly taken into consideration one of the inner maximum-living shark species, placed at depths of as much as as a minimum one, hundred meters.
Are deep sea sharks risky to humans?
Most deep sea sharks aren’t a chance to human beings. They usually inhabit deep waters some distance from human hobby.
How can we help guard deep sea sharks?
You can assist defend deep sea sharks with the resource of supporting conservation groups, advocating for sustainable fishing practices, and decreasing plastic use to decrease ocean pollution.
What do deep sea sharks consume?
Deep sea sharks in maximum instances feed on fish, squid, and plankton, depending on their species and habitat.
Why are deep sea sharks called “dwelling fossils”?
Many deep sea sharks, consisting of the Goblin and Frilled Sharks, have remained exceptionally unchanged for millions of years, earning them the name of “living fossils.”
Conclusion
Deep sea sharks are critical to our oceans’ health and range. Despite their importance, they face numerous threats from human sports.
Understanding and shielding those great creatures is crucial for maintaining the stability of marine ecosystems.
Through collective efforts, we’re able to ensure a future wherein deep sea sharks keep to thrive within the depths of the sea.



